The journey through pregnancy is an exciting and transformative experience for expecting parents. Along with the joy and anticipation, there's also a natural concern for the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. Prenatal testing plays a crucial role in providing valuable information about the baby's health, and one such advanced screening method is Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT). In this blog post, we will explore the NIPT test, its significance, and what expecting parents should know about this innovative screening option.
What is NIPT?
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing, commonly known as NIPT, is a cutting-edge screening method used to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus during early pregnancy. Unlike traditional methods that carry a small risk of miscarriage, NIPT is a non-invasive procedure that poses no direct harm to the baby or the mother. It is typically performed between the 10th and 13th week of pregnancy.
How Does NIPT Work?
NIPT primarily analyzes cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in the maternal bloodstream. During pregnancy, a small amount of the baby's DNA circulates in the mother's blood. NIPT isolates and examines this fetal DNA to identify any potential chromosomal abnormalities. The most common conditions screened for include
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)
Advantages of NIPT:
- Accuracy: NIPT has shown high accuracy rates in detecting chromosomal abnormalities, reducing the need for further invasive diagnostic procedures.
- Non-Invasive: As a blood test, NIPT eliminates the risk of miscarriage associated with invasive procedures like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
- Early Detection: NIPT can be performed earlier in pregnancy, providing expecting parents with valuable information at an earlier stage.
In India, NIPT is becoming more popular due to various factors such as increasing awareness, delayed pregnancy. NIPT is a screening test that estimates the risk of certain genetic abnormalities in the fetus by analyzing the mother’s blood. It cannot detect all types of congenital defects. Therefore, ACMG guidelines do not recommend it for pregnancies with known complications or malformations.
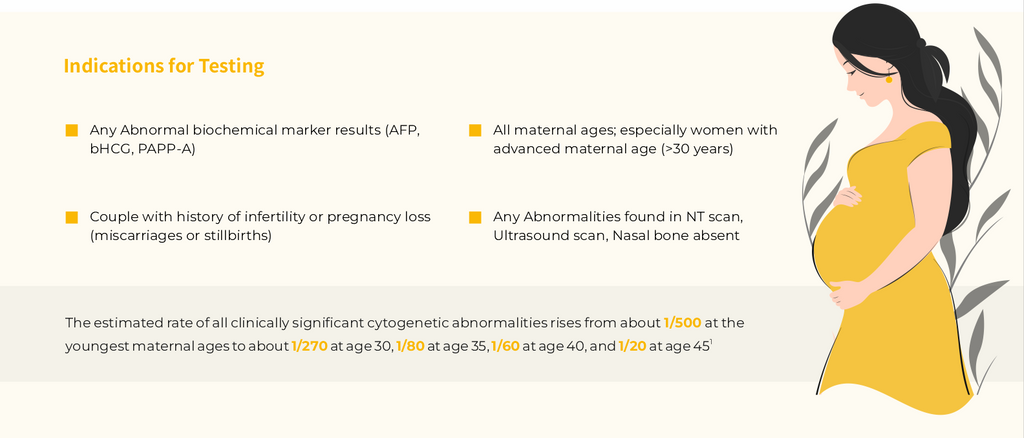
Hook E. B. (1981). Rates of chromosome abnormalities at different maternal ages. Obstetrics and gynecology, 58(3), 282–285.
Mapmygenome's Babymap portfolio includes three NIPT tests: Babymap Basic, Babymap Plus, and Babymap Advanced. These tests cover different levels of screening for chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions.
Babymap Basic screens for trisomy 21, 18, and 13, and sex chromosome aneuploidies. Babymap Plus screens for trisomy 21, 18, and 13, sex chromosome aneuploidies, and five common microdeletions: 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome), 1p36 deletion syndrome, cri-du-chat syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome/Angelman syndrome, and Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Babymap Advanced screens for trisomy 21, 18, and 13, sex chromosome aneuploidies, five common microdeletions, and rare autosomal aneuploidies.
Mapmygenome's Babymap tests are validated on Indian samples and offer high accuracy, fast turnaround time, low test failure rate, and free genetic counseling. Mapmygenome's Babymap tests can help parents planning a baby to have a safe and healthy pregnancy journey.
Counseling and Informed Decision-Making:
Before opting for NIPT, it's crucial for expecting parents to undergo genetic counseling. This involves discussing the test's purpose, potential outcomes, and the implications of the results. Informed decision-making ensures that parents are aware of the limitations and benefits of NIPT, empowering them to make choices aligned with their values and preferences.