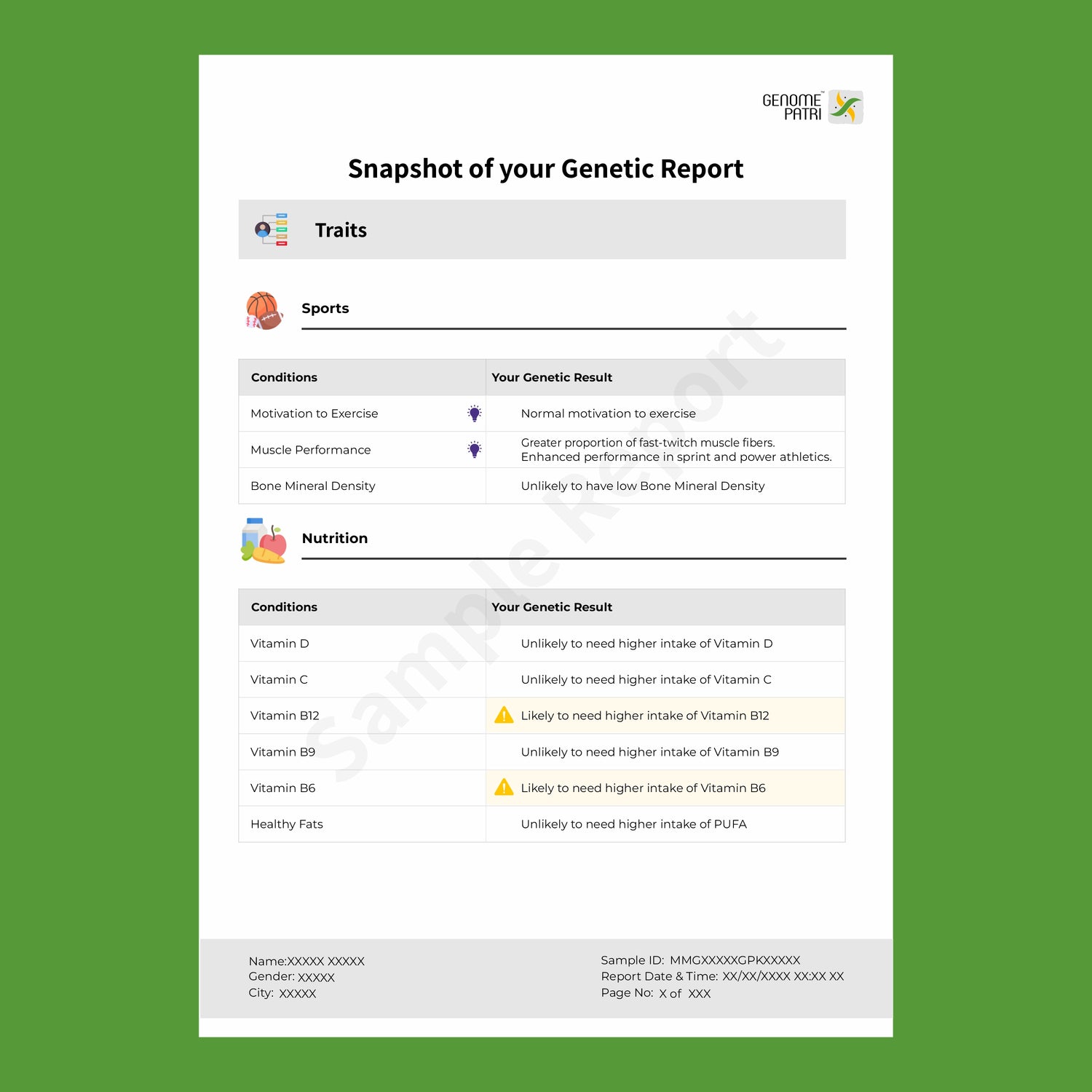
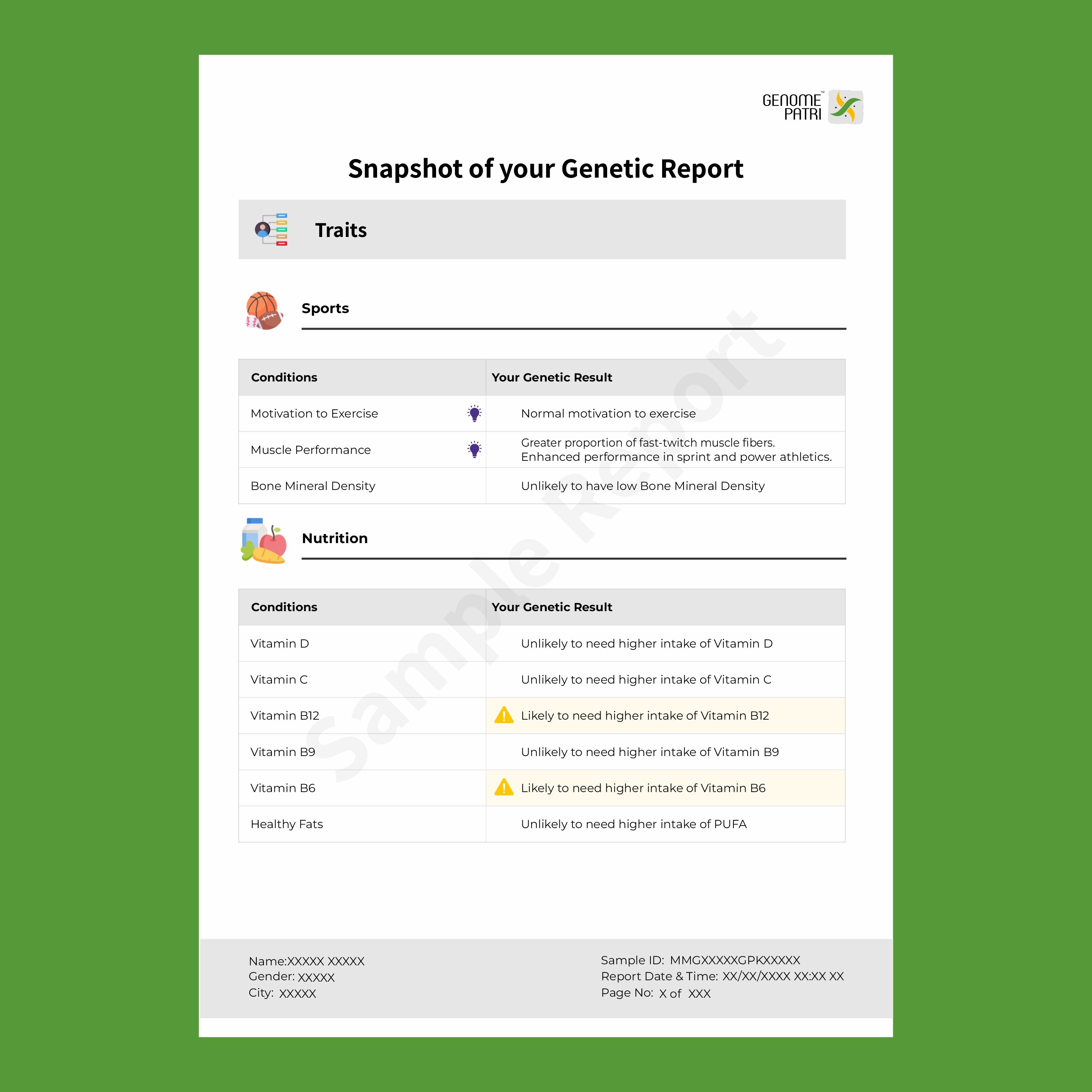
In today’s world, understanding your family’s health history is more important than ever. Genetic testing has revolutionized how we identify and manage inherited diseases, making it easier to take control of your health and your family’s future.
This blog dives into the role of genetic testing in identifying hereditary conditions, its benefits, and how it can empower you to make informed health decisions.
What Are Inherited Diseases?
Inherited diseases are medical conditions passed down from one generation to the next through genes. These conditions arise from genetic mutations or variations that are transmitted within a family. Common examples include:
- Cystic fibrosis
- Huntington’s disease
- Sickle cell anemia
- BRCA-related breast and ovarian cancers
Understanding your family history is the first step in identifying whether you might carry the genetic markers for such disorders.
Why Your Family History Matters
Your family history is like a health blueprint, showing patterns that could indicate inherited risks. If close relatives have had a genetic disorder, your chances of developing or passing it on may be higher.
Did You Know?
- If your parents are carriers of a recessive genetic condition, there’s a 25% chance you could inherit the disorder.
- Some conditions, like BRCA-related cancers, are linked to dominant mutations, meaning even one copy of the faulty gene can increase your risk significantly.
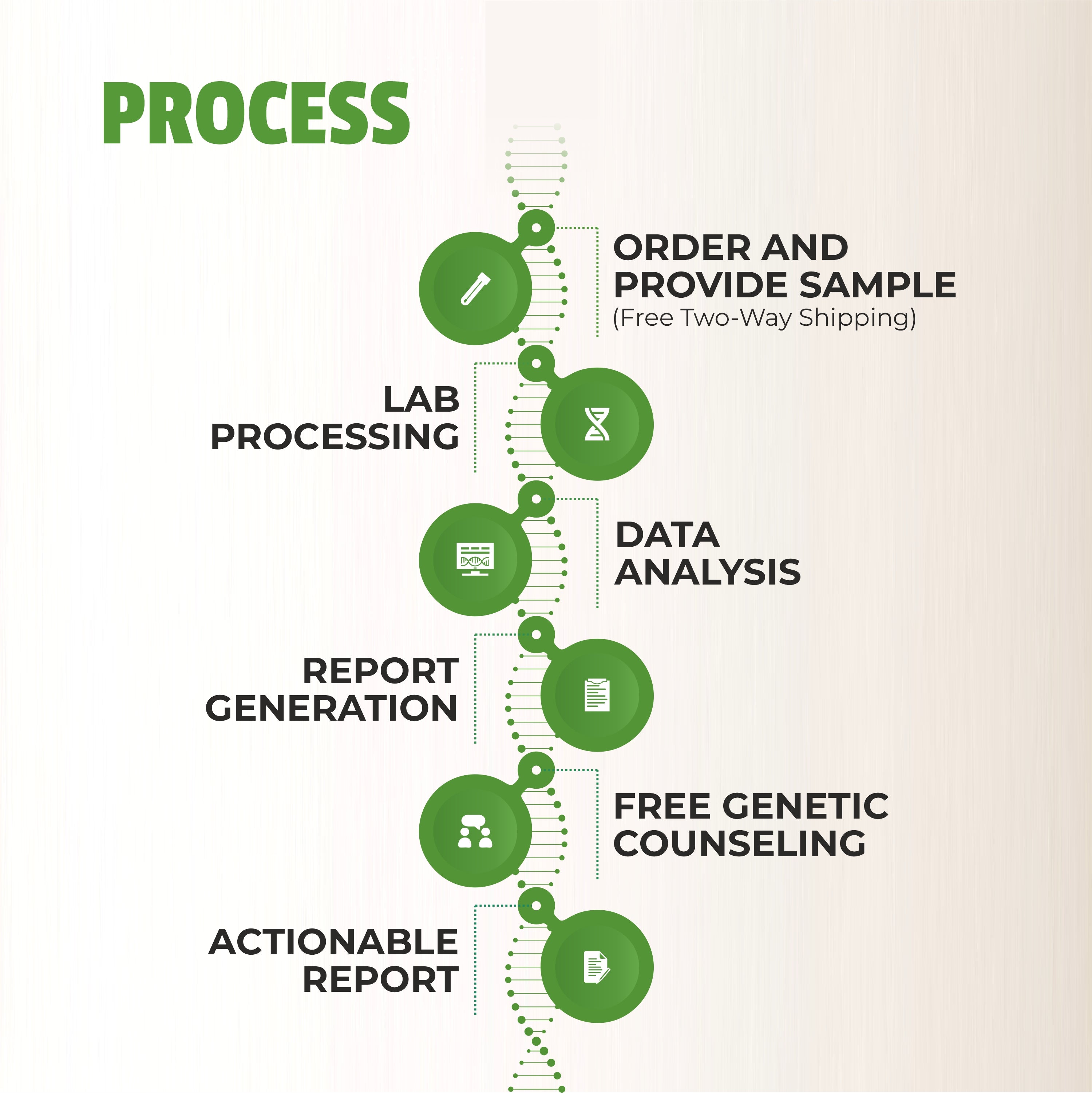
How Genetic Testing Works
Genetic testing analyzes your DNA to identify mutations associated with inherited diseases. The process typically involves:
- Counseling: A session with a genetic counselor to discuss your family history and testing goals.
- Sample Collection: A simple blood or saliva sample.
- Laboratory Analysis: Advanced tools like genetic disorders testing panels identify mutations in specific genes.
- Results Interpretation: A genetic counselor explains your results and potential next steps.
Types of Genetic Tests for Inherited Conditions
1. Carrier Screening
Identifies whether you’re a carrier of a genetic condition, especially important for couples planning a family.
2. Predictive Testing
Helps assess the likelihood of developing a genetic condition in the future.
3. Diagnostic Testing
Confirms whether symptoms you’re experiencing are linked to a genetic disorder.
4. Prenatal Testing
Screens for genetic conditions in unborn babies, providing early insights.
5. Newborn Screening
Detects genetic conditions in infants shortly after birth to enable early interventions.
Benefits of Genetic Testing for Inherited Conditions
- Early Detection: Identify potential health risks before symptoms appear.
- Personalized Care Plans: Tailor treatments and lifestyle changes to manage risks.
- Informed Family Planning: Make informed decisions about starting or growing your family.
- Preventive Measures: Reduce your risk with lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical options.
- Emotional Relief: Gain clarity and peace of mind about your health.
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing?
You might want to consider genetic disorders testing if:
- You have a family history of inherited diseases.
- You’re planning to start a family and want to ensure healthy pregnancies.
- You’ve been diagnosed with a condition that might have a genetic link.
- You belong to an ethnic group with a higher prevalence of specific genetic disorders.
Advancements in Genetic Testing
Genetic testing has come a long way, thanks to cutting-edge technologies like next-generation sequencing (NGS) and artificial intelligence. These advancements:
- Make tests faster and more accurate.
- Enable the analysis of multiple genes simultaneously.
- Improve accessibility and affordability.
Genetic Counseling: Your Guide Through the Process
Genetic counseling is a critical part of the genetic testing journey. A trained counselor can:
- Help you understand your family history.
- Explain what your test results mean.
- Provide support for next steps, whether it’s further testing, medical management, or preventive strategies.
Actionable Steps to Take
- Gather Your Family Health History: Talk to relatives to identify patterns of inherited conditions.
- Consult a Genetic Counselor: Seek professional advice tailored to your situation.
- Choose the Right Test: Work with experts to select tests that align with your health goals.
- Take Preventive Actions: Based on your results, adopt a healthier lifestyle or medical interventions.
FAQs About Genetic Testing for Inherited Conditions
1. What is genetic testing?
Genetic testing analyzes your DNA to detect mutations or variations that may lead to inherited diseases.
2. How do I know if I need genetic testing?
If you have a family history of inherited diseases or belong to an at-risk group, genetic testing may be beneficial.
3. Is genetic testing expensive?
Costs vary depending on the type of test and your location. Many tests are now more affordable, and some may be covered by insurance.
4. Can genetic testing predict all diseases?
No, genetic testing identifies risks for specific inherited conditions but cannot predict all diseases.
5. Is my genetic data private?
Yes, reputable testing providers ensure strict confidentiality and compliance with data protection laws.
6. What if my test results are positive?
Positive results don’t mean you will develop the condition, but they indicate a higher risk. A genetic counselor can guide your next steps.
The Future of Family Health
Genetic testing empowers you to take charge of your health and that of future generations. By understanding your family history and exploring genetic disorders testing, you can make proactive choices to safeguard your well-being.
Your journey to a healthier future starts with knowledge. Take that first step today!
Conclusion
Genetic testing is more than just a tool for understanding your DNA—it’s a pathway to a healthier, informed future for you and your family. With the advancements in genetic testing technology and the support of genetic counseling, you can tackle inherited diseases head-on.
Remember, your health matters—and so does your family’s.