Heart attacks are a leading cause of death worldwide, making it crucial to recognize their symptoms and seek prompt medical attention. Whether you're concerned about your heart health or simply want to be prepared, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the signs of a heart attack and what steps to take if you or someone else experiences them.
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked for an extended period, causing damage or death to the heart tissue. This blockage is usually due to a buildup of fat, cholesterol, and other substances forming a plaque in the coronary arteries.
Common Heart Attack Symptoms
Heart attack symptoms can vary between individuals and may present differently in men and women. However, the most common symptoms include:
-
Chest Pain or Discomfort:
- Often described as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest.
- This sensation can last for more than a few minutes or come and go.
-
Upper Body Pain:
- Pain or discomfort may radiate to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
-
Shortness of Breath:
- May occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Can happen at rest or during physical activity.
-
Cold Sweats:
- Unexpected sweating or breaking out in a cold sweat.
-
Nausea or Vomiting:
- Feeling nauseous or experiencing vomiting can also be a symptom.
-
Lightheadedness or Dizziness:
- Feeling faint or dizzy can be a sign of a heart attack.
Heart Attack Symptoms in Women
Women may experience some heart attack symptoms differently than men. While chest pain is still the most common symptom, women are more likely to report:
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Back or jaw pain
- Unexplained fatigue
These differences highlight the importance of recognizing a broader range of symptoms to ensure timely medical intervention.
Silent Heart Attacks
Not all heart attacks present with obvious symptoms. Some may occur without noticeable chest pain, known as silent heart attacks. These are particularly common in people with diabetes and can be identified through routine medical examinations and tests like electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Risk Factors for Heart Attacks
Understanding the risk factors can help you take proactive steps to reduce your risk. Key risk factors include:
- High Blood Pressure: Damages arteries over time, making them more susceptible to blockages.
- High Cholesterol: Leads to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Smoking: Contributes to artery damage and reduces oxygen in the blood.
- Diabetes: Increases the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Obesity: Strains the heart and can lead to high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is a significant risk factor.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase your risk.
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially for men over 45 and women over 55.
- Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease.
What to Do if You Suspect a Heart Attack
If you or someone else exhibits symptoms of a heart attack, it is vital to act quickly. Here are the steps to take:
-
Call Emergency Services:
- Dial your local emergency number immediately. Time is critical in treating a heart attack.
-
Chew Aspirin:
- If the person is not allergic and can chew, give them an aspirin to help thin the blood.
-
Stay Calm and Rest:
- Keep the person calm and encourage them to sit or lie down while waiting for emergency responders.
-
Perform CPR:
- If the person becomes unconscious and unresponsive, begin CPR if you are trained.
Preventing Heart Attacks
While some risk factors like age and family history cannot be changed, many lifestyle modifications can help reduce your risk of a heart attack:
-
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet:
- Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
-
Exercise Regularly:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
- Include cardiovascular, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
-
Quit Smoking:
- Seek support to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Strive for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
-
Manage Stress:
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
-
Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol:
- Regularly check your blood pressure and cholesterol levels and manage them with diet, exercise, and medication if needed.
-
Control Diabetes:
- Keep blood sugar levels under control with a healthy diet, exercise, and medications as prescribed.
-
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all.
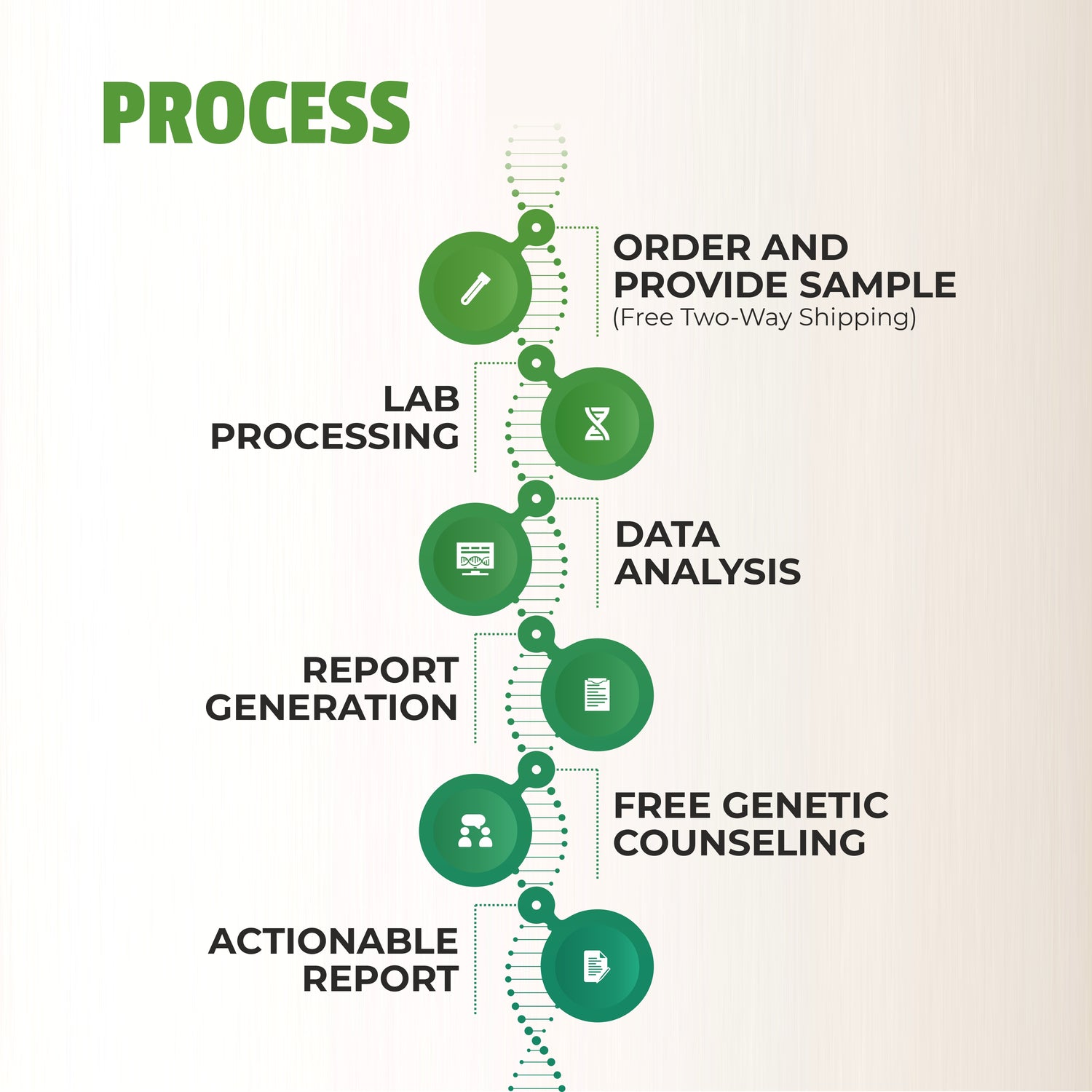
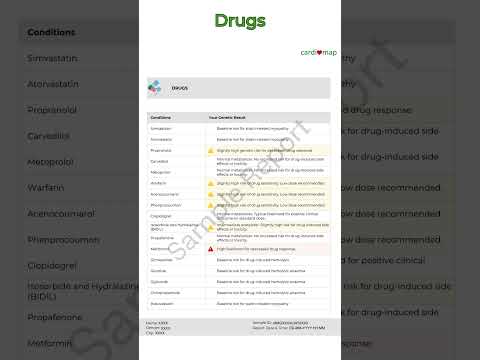
The Role of Genetic Testing
Understanding your genetic predisposition to heart disease can provide valuable insights into your risk factors and help you take proactive measures. Companies like MapmyGenome offer genetic testing services such as Cardiomap, which analyzes your genetic makeup to identify potential health risks, including those related to heart disease. This personalized approach allows for more tailored prevention and treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack and understanding your risk factors can significantly improve your chances of prevention and early intervention. By making lifestyle changes, managing existing health conditions, and considering genetic testing, you can take control of your heart health and reduce your risk of a heart attack. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and regular check-ups to stay on top of your heart health. Remember, knowledge and proactive care are your best allies in maintaining a healthy heart.