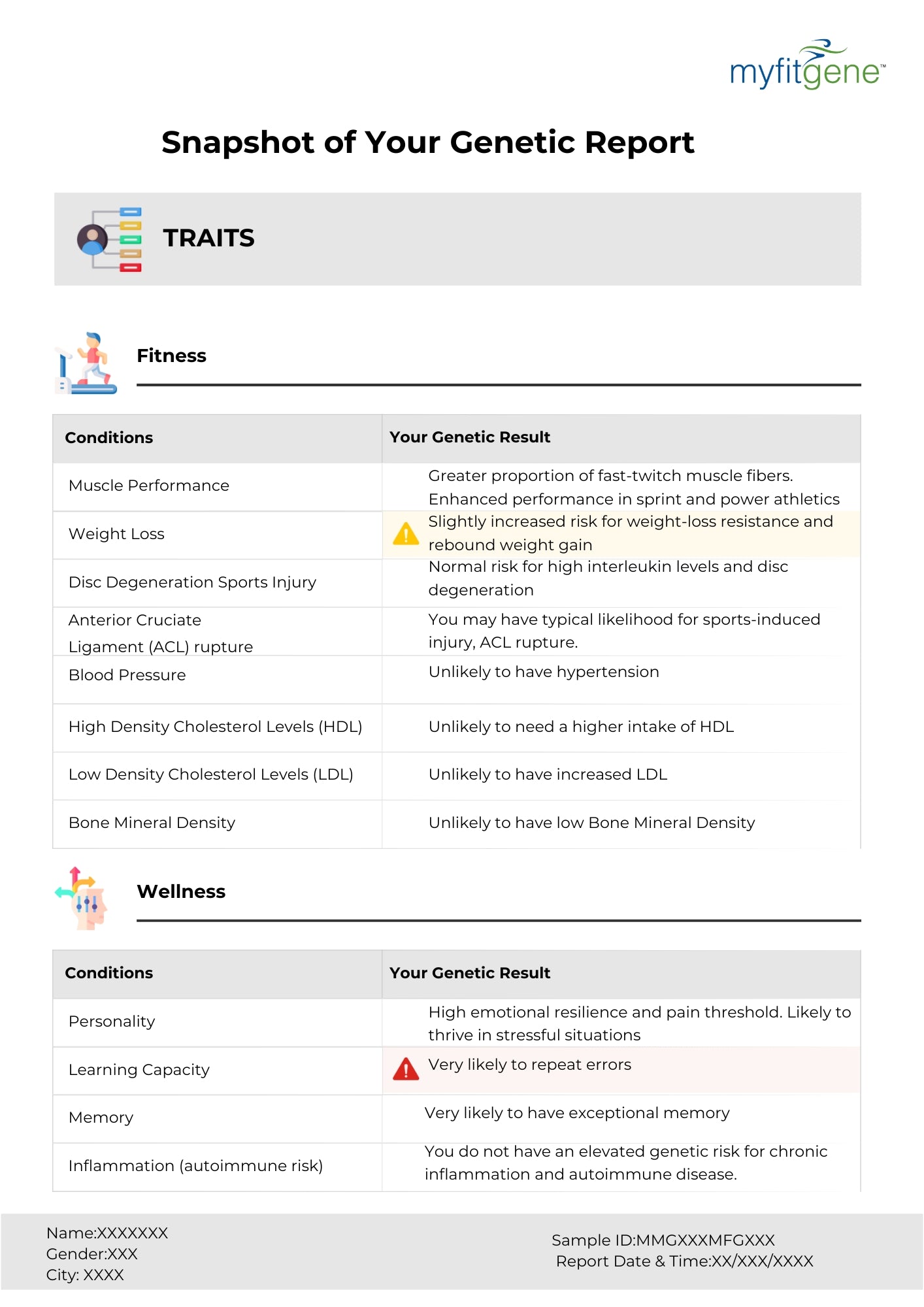
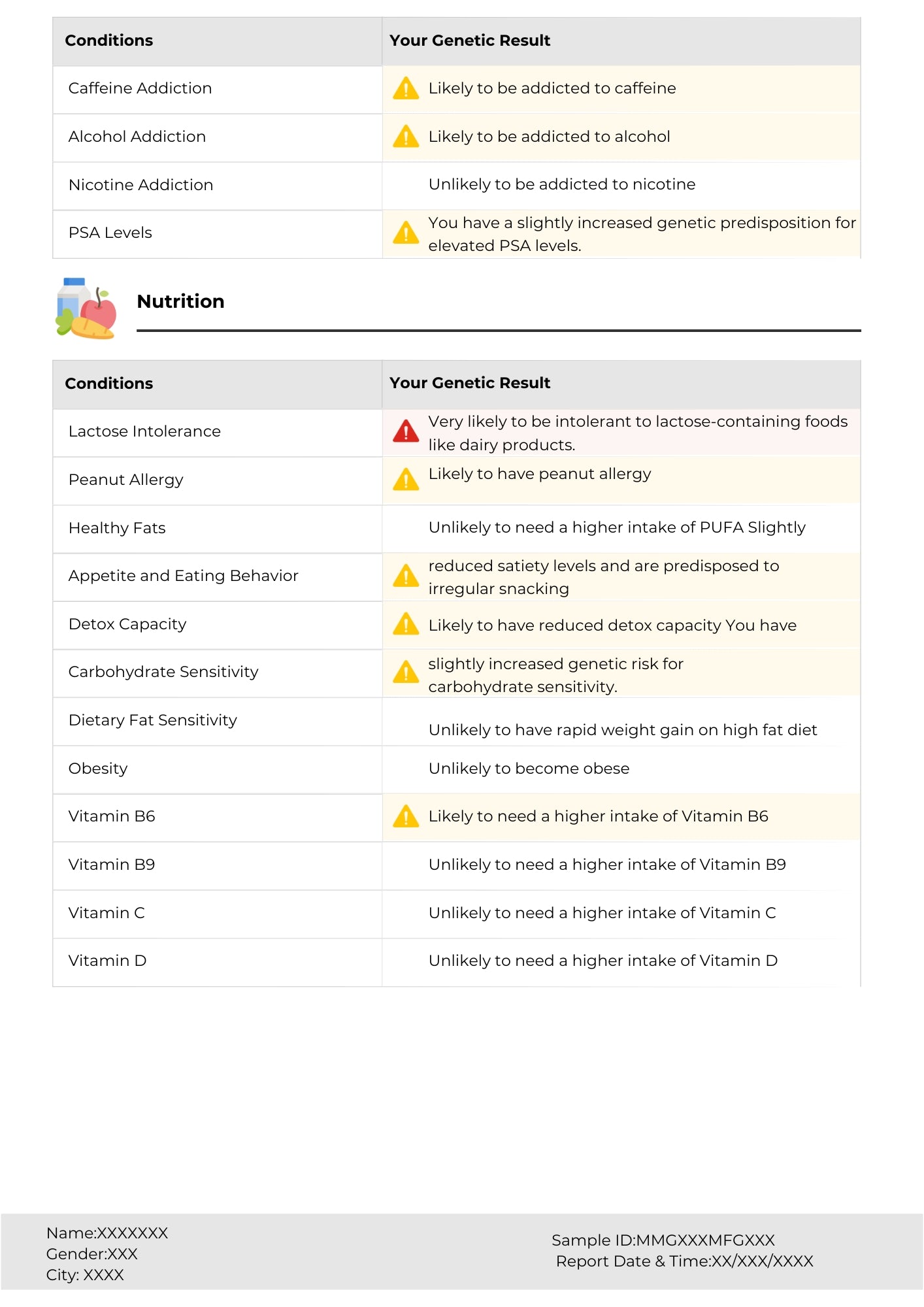
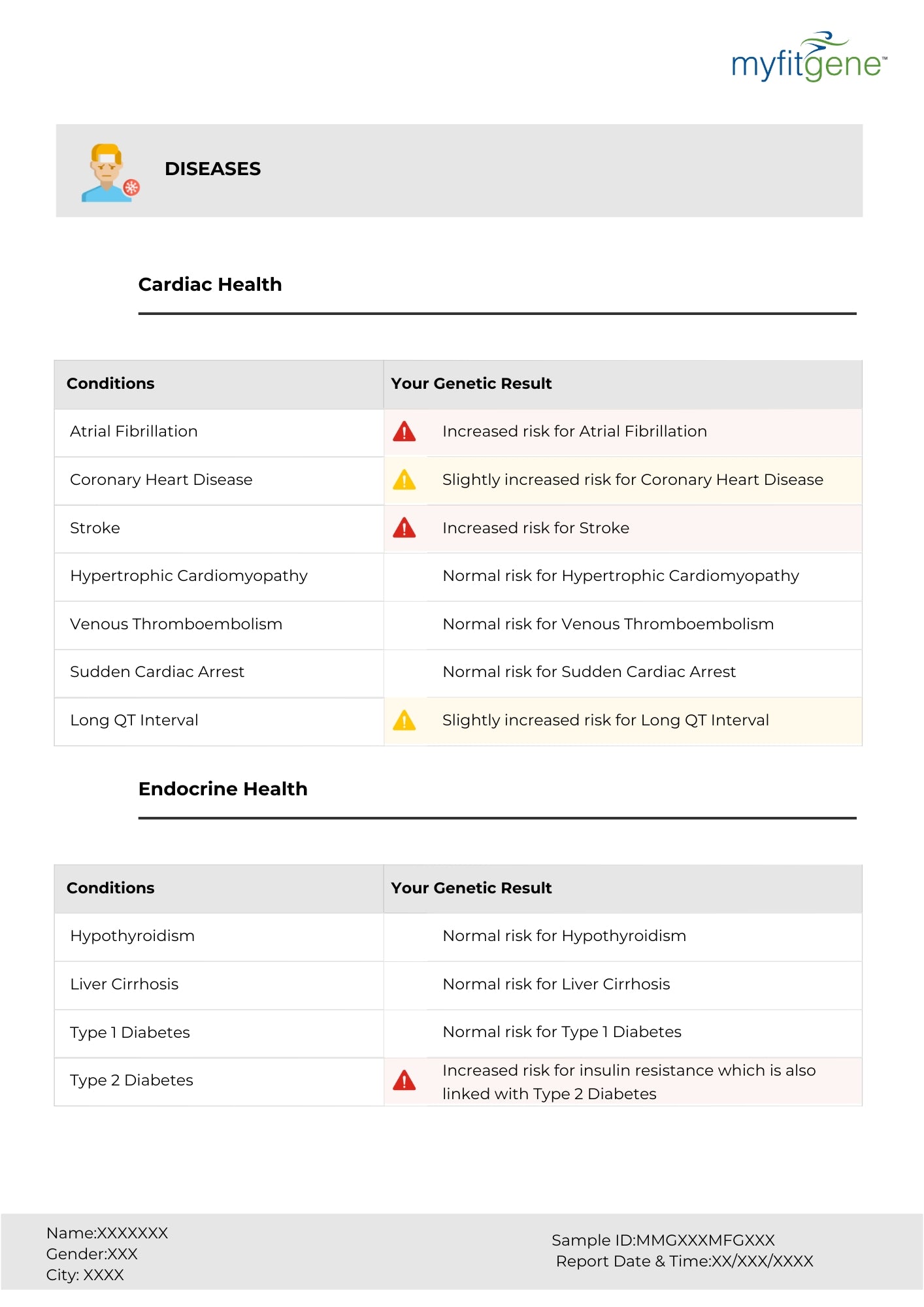
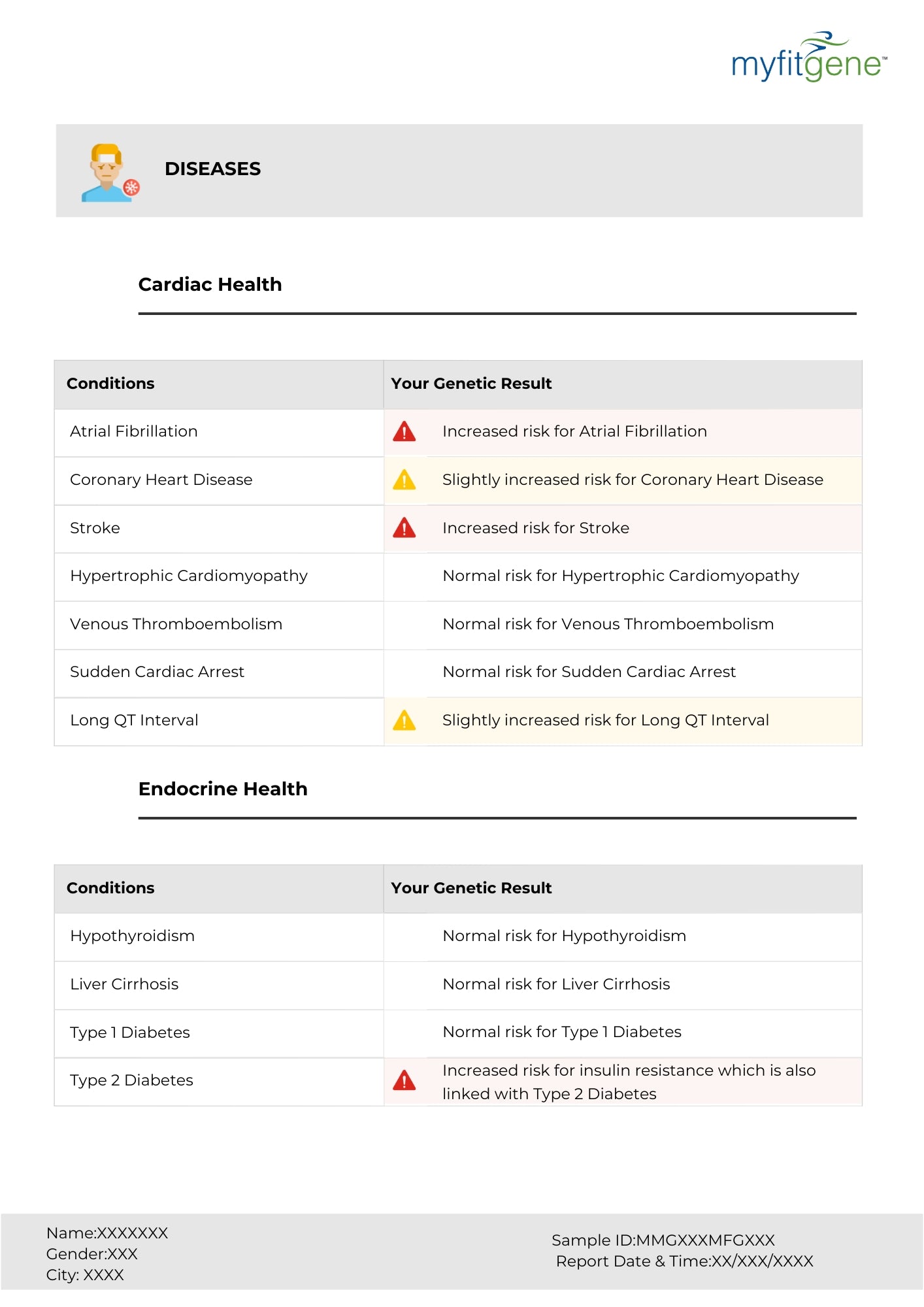
"Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food." – Hippocrates
This ancient wisdom holds especially true when it comes to protein, the essential building block of life. Proteins are crucial for growth, repair, and the maintenance of almost every part of our bodies. But there’s more to these complex molecules than meets the eye, and they’re not without controversy. Let’s explore the fascinating world of protein!
What Are Proteins?
Think of proteins as long chains of amino acids, the building blocks of life. There are 20 different amino acids, and their arrangement determines the function of each protein. Some proteins provide structure (like collagen in your skin), others act as enzymes (speeding up chemical reactions), and some serve as hormones (chemical messengers).
Protein Sources: Beyond the Steak
"The doctor of the future will no longer treat the human frame with drugs, but rather will cure and prevent disease with nutrition." – Thomas Edison
While meat is a traditional protein source, the protein spectrum is much broader:
Animal Sources:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, beef)
- Fish and seafood
- Eggs
- Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
Plant Sources:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Nuts and seeds
- Quinoa
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale)
Protein Facts: Did You Know?
- Beyond Muscles: Protein is not just for muscle growth and repair. It plays roles in immune function, hormone production, and oxygen transport in your blood.
- Quality Matters: Your body can make some amino acids (non-essential), but nine essential amino acids must come from your diet. Animal proteins typically provide all essential amino acids, whereas plant proteins might lack one or two, highlighting the importance of a varied diet, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
- Cooking Effects: Overcooking can damage proteins, making them less digestible. Opt for gentle cooking methods like steaming, poaching, or baking.
- Genetic Influence: Your genes can affect how efficiently you digest and use proteins, influencing your body’s response to different types and amounts of protein.
Controversies in the Protein World
"One man’s food is another man’s poison." – Lucretius
The protein debate includes:
- High-Protein Diets: Advocates claim benefits for weight loss, muscle building, and metabolism, but concerns exist about potential kidney strain and other long-term health effects.
- Protein Timing: Research varies on whether spreading protein intake throughout the day or consuming larger amounts post-workout is more beneficial.
- Plant vs. Animal Protein: The debate over whether plant proteins are as "complete" as animal proteins continues. While plant proteins are nutritious, they may be lower in certain essential amino acids.
- Protein Supplements: The necessity and effectiveness of protein supplements are debated. Whole food sources are often preferred for their comprehensive nutritional benefits.
Your Microbiome: A Reflection of Your Diet
"The gut microbiome is like a rainforest – a diverse ecosystem that thrives on balance."
Our gut microbiome, a vast community of microbes in our digestive tract, reflects our dietary habits. A diet rich in fiber and plant-based foods promotes a healthy microbiome, while a diet high in processed foods and sugar can harm it. Research is uncovering the link between our microbiome and health, including protein digestion and metabolism. By analyzing gut bacteria, we can gain insights into how our bodies process protein and make dietary adjustments for optimal health.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Determining your protein needs depends on factors like age, sex, activity level, health, genetics, and dietary preferences. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is the best way to determine your individual protein requirements.
Let’s Talk Protein!
Do you have favorite protein-rich recipes or tips for meeting your protein needs? Share them with us! Let’s make protein a delicious, nutritious, and thought-provoking part of our lives.