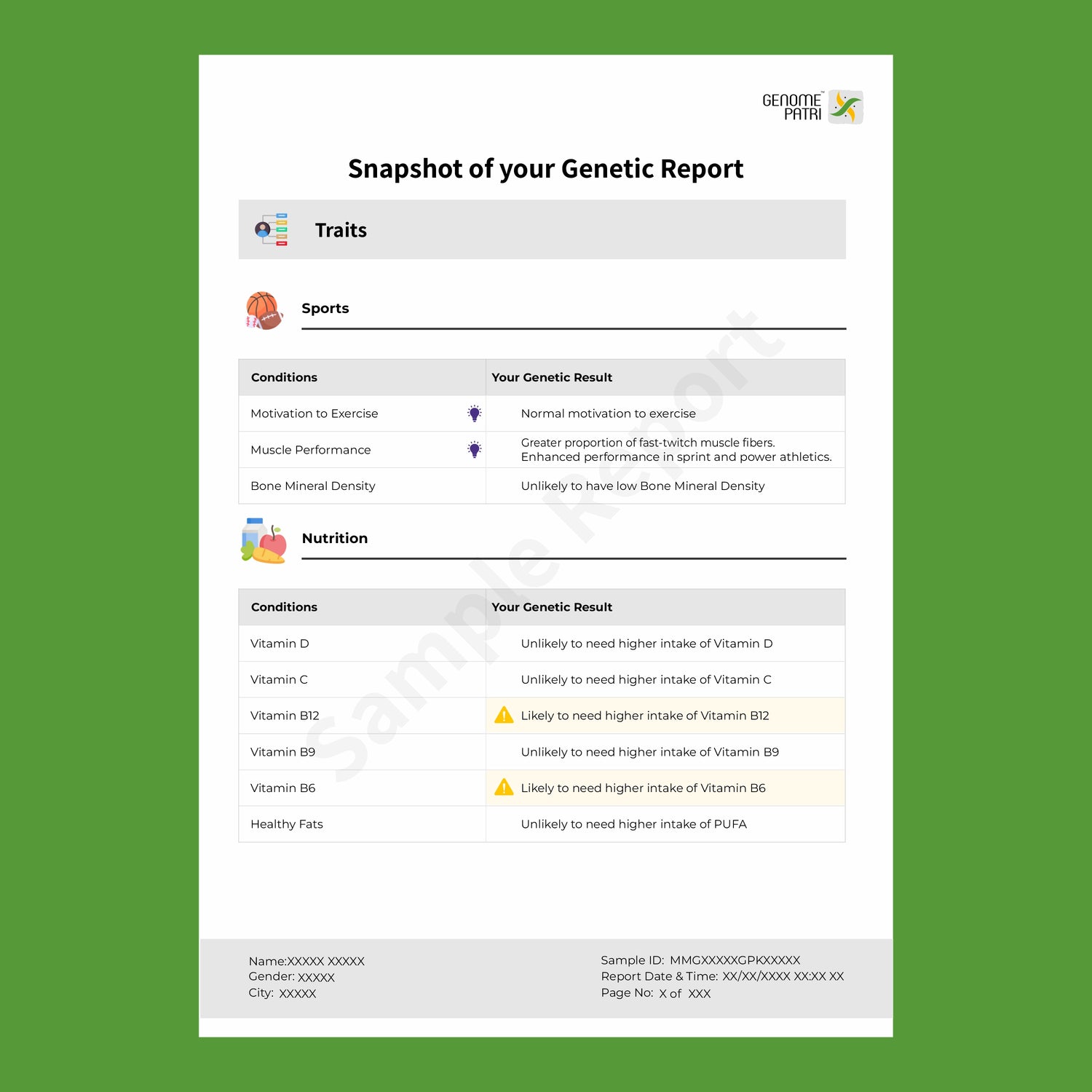
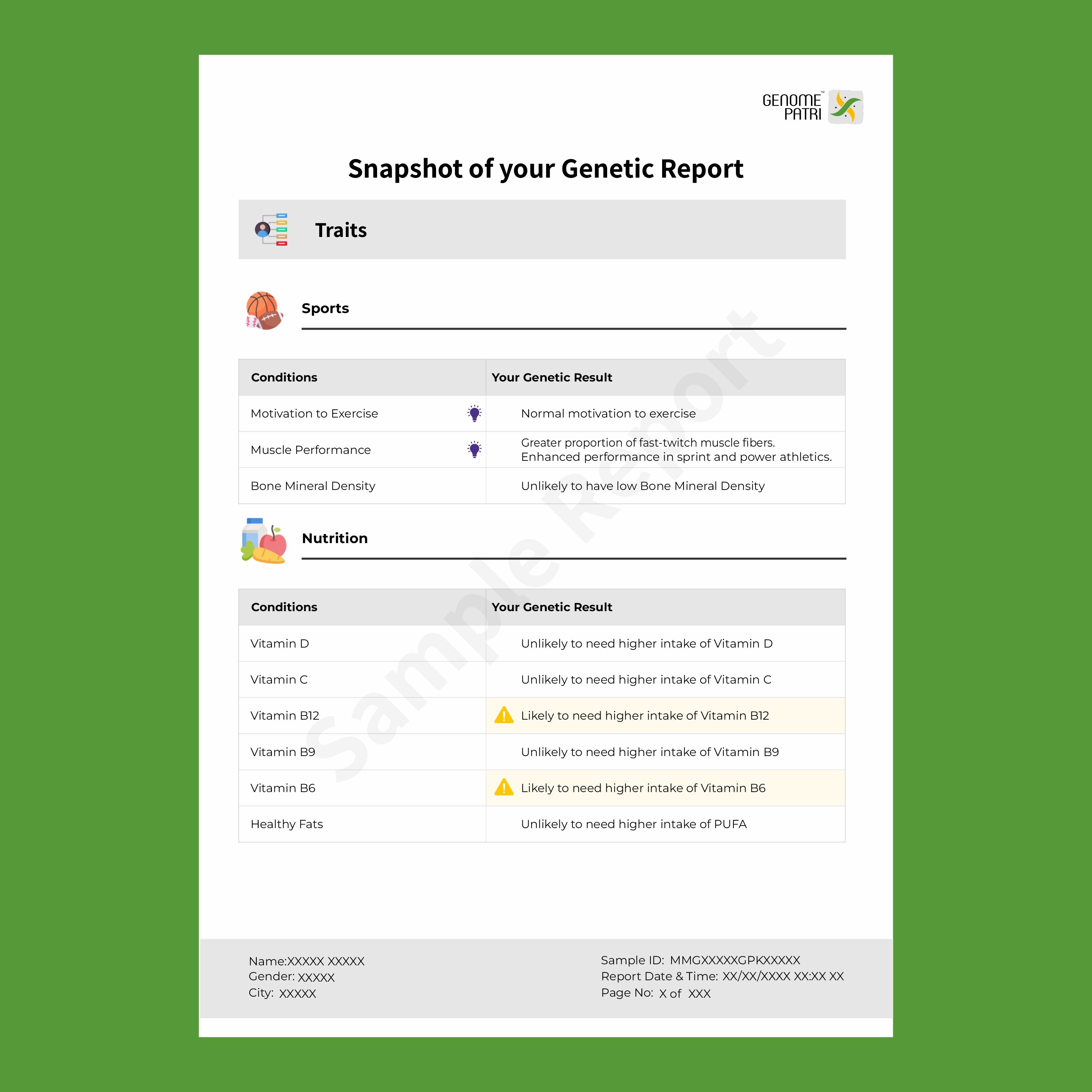
In today’s fast-paced world, healthcare is increasingly shifting from reactive treatment to proactive prevention. This paradigm shift emphasizes the importance of identifying potential health risks before they develop into serious conditions. One of the most powerful tools in this preventive approach is genetic testing. By analyzing an individual's DNA, genetic testing can provide invaluable insights into their risk of developing certain diseases, allowing for early intervention and personalized healthcare strategies.
Understanding Preventive Healthcare
Preventive healthcare is a strategy focused on maintaining health and well-being by preventing diseases before they occur. This approach includes regular check-ups, vaccinations, screenings, and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Traditionally, preventive measures have been based on general guidelines, but advancements in genetic research are paving the way for more personalized preventive strategies.
-
The Evolution of Preventive Healthcare:
Historically, preventive healthcare relied on a one-size-fits-all model, with recommendations based on factors like age, gender, and family history. While these factors are important, they don’t account for individual variations at the genetic level. Genetic testing adds a new dimension to preventive healthcare by providing insights tailored to each person’s unique genetic makeup. -
What is Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing involves analyzing DNA to identify variations or mutations that may increase the risk of certain diseases. These tests can reveal whether a person has inherited genetic mutations associated with specific conditions, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 for breast and ovarian cancer, or the APC gene for familial adenomatous polyposis, a condition that significantly increases the risk of colorectal cancer. By understanding these risks, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent or detect diseases early.
The Benefits of Genetic Testing in Preventive Healthcare
Genetic testing offers several key benefits that can significantly enhance preventive healthcare efforts:
-
Early Detection of Genetic Disorders:
One of the most compelling benefits of genetic testing is the ability to detect genetic predispositions to certain diseases long before symptoms appear. For example, if a genetic test reveals that an individual carries a mutation in the BRCA1 gene, which significantly increases the risk of breast and ovarian cancer, they can undergo more frequent screenings, adopt lifestyle changes, or even consider preventive surgeries to reduce their risk. Early detection and intervention can be lifesaving, especially for conditions that are challenging to treat in their advanced stages. -
Personalized Medicine:
Genetic testing is a cornerstone of personalized medicine, an approach that tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. By understanding a patient’s genetic profile, healthcare providers can recommend targeted prevention strategies, such as specific medications, lifestyle modifications, or surveillance programs. For instance, individuals with a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol may benefit from early statin therapy and dietary changes to prevent cardiovascular disease. Personalized medicine ensures that preventive measures are not only effective but also specifically aligned with the patient’s genetic risk factors. -
Informed Family Planning:
Genetic testing can also play a vital role in family planning by identifying carriers of genetic mutations that could be passed on to future generations. For couples planning to have children, genetic testing can assess the risk of inherited conditions such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or Tay-Sachs disease. Armed with this knowledge, couples can make informed decisions about family planning, including options like preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) during IVF, adoption, or the use of donor eggs or sperm. This proactive approach can help prevent the transmission of serious genetic conditions and ensure healthier outcomes for future generations. -
Empowerment and Peace of Mind:
Knowledge is power, and genetic testing empowers individuals by providing them with detailed information about their health risks. This knowledge can lead to greater peace of mind, as individuals who test negative for certain genetic mutations can be reassured about their risk levels. Conversely, those who test positive can take control of their health by working with their healthcare providers to develop a proactive plan for monitoring and prevention. By taking action early, individuals can reduce their anxiety about the unknown and feel more confident about their future health.
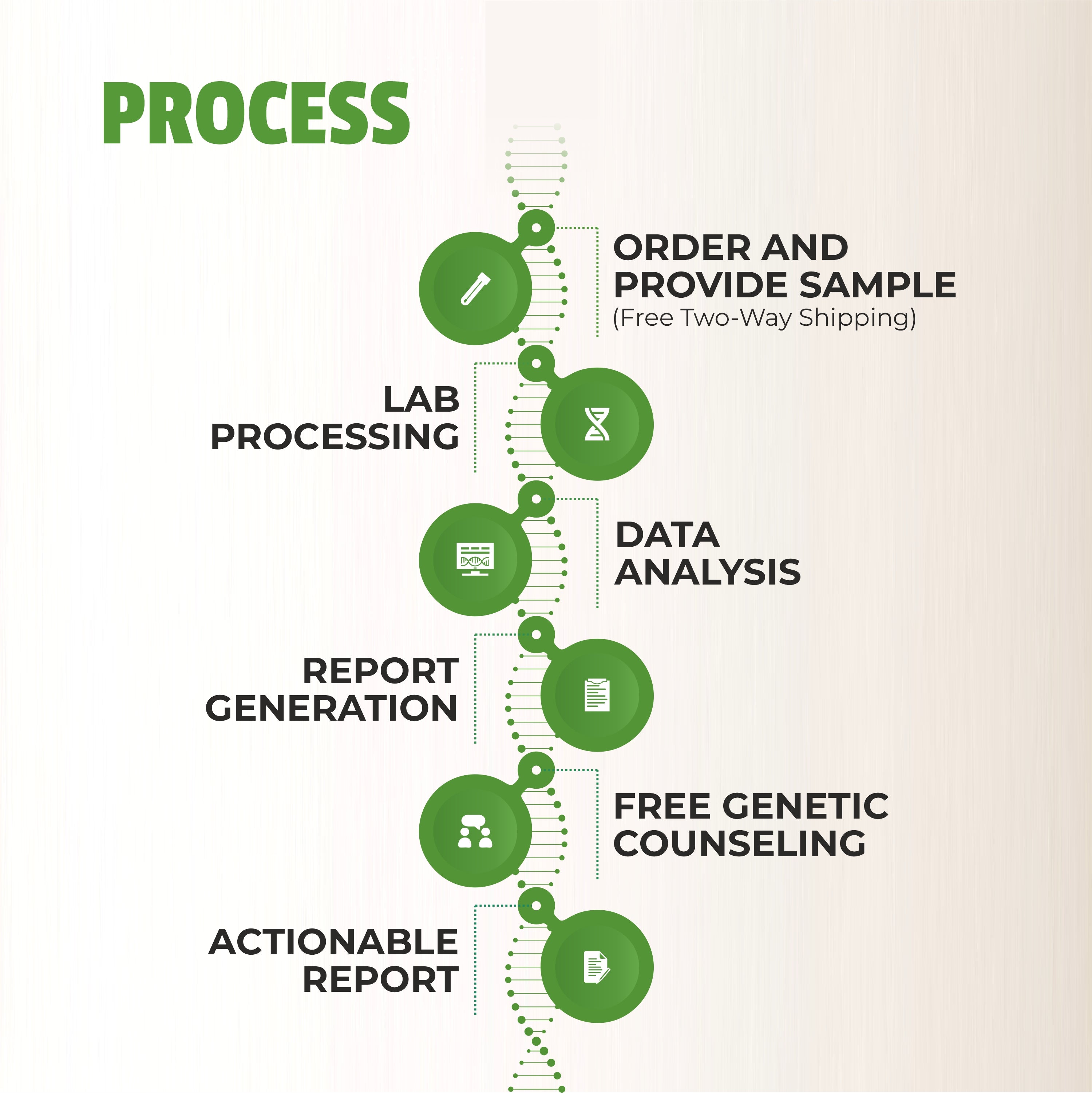
How Genetic Testing Works: A Simple Overview
The process of genetic testing is straightforward and typically involves the following steps:
-
Consultation:
The first step is usually a consultation with a healthcare provider or genetic counselor who will discuss your family history, personal health concerns, and the potential benefits of genetic testing. This consultation helps determine whether genetic testing is appropriate for you and which specific tests might be most beneficial. -
Sample Collection:
Genetic testing requires a sample of your DNA, which can be collected through a simple blood draw, saliva sample, or cheek swab. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. -
DNA Analysis:
In the lab, your DNA is analyzed to identify specific genetic mutations or variations that may increase your risk of certain diseases. The analysis can take several weeks, depending on the complexity of the test. -
Results and Interpretation:
Once the analysis is complete, your healthcare provider or genetic counselor will explain the results to you. They will discuss what the findings mean for your health and recommend any necessary preventive measures or further testing. -
Follow-Up:
Genetic testing is just the beginning of a proactive health plan. Based on the results, your healthcare provider will work with you to implement preventive strategies, which may include lifestyle changes, regular screenings, or medications. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor your health and adjust your preventive plan as needed.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
While genetic testing offers numerous benefits, it also raises important ethical considerations and has certain limitations:
-
Privacy and Data Security:
Genetic information is highly sensitive, and there are concerns about how this data is stored, shared, and used. It's crucial to choose a reputable provider that adheres to strict privacy and security standards to protect your genetic information. -
Genetic Discrimination:
Although laws like the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) in the U.S. provide some protections against discrimination based on genetic information, concerns remain. Individuals may worry about potential discrimination by employers or insurance companies based on their genetic risk factors. -
Interpretation of Results:
Not all genetic mutations are fully understood, and the interpretation of genetic testing results can be complex. There is also the possibility of receiving inconclusive results, which can be frustrating or anxiety-inducing. This is why genetic counseling is an essential component of the testing process, as it helps individuals understand and cope with their results. -
Cost and Accessibility:
The cost of genetic testing can be a barrier for some individuals, and not all insurance plans cover these tests. Additionally, access to genetic testing and counseling may be limited in certain regions, particularly in underserved communities. Ensuring equitable access to genetic testing is crucial for its widespread adoption as a preventive healthcare tool.
Conclusion: Taking the First Step Toward Preventive Healthcare
Preventive healthcare is about taking control of your health before problems arise, and genetic testing is a powerful tool in this proactive approach. By understanding your genetic risks, you can work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that addresses potential health issues before they become serious. Whether it’s monitoring for early signs of cancer, managing cholesterol levels, or planning for a healthy family, genetic testing can provide the insights you need to live a longer, healthier life.
If you’re considering genetic testing, start by having a conversation with your healthcare provider. Together, you can determine whether genetic testing is right for you and how it can fit into your overall preventive healthcare strategy. By taking this important step, you’re not just safeguarding your health today—you’re investing in a healthier future.