Genetic testing for children is a growing area of healthcare, offering valuable insights into potential health risks before symptoms manifest. For parents, understanding their child's genetic predispositions can be a game-changer, helping in early detection and preventive care. From assessing hereditary conditions to identifying risk factors for common and rare diseases, genetic testing empowers families to make informed decisions about their child's health.
In this blog, we will explore the benefits of genetic testing for children, how it works, and why it can play a crucial role in safeguarding your child's future.
What Is Genetic Testing for Children?
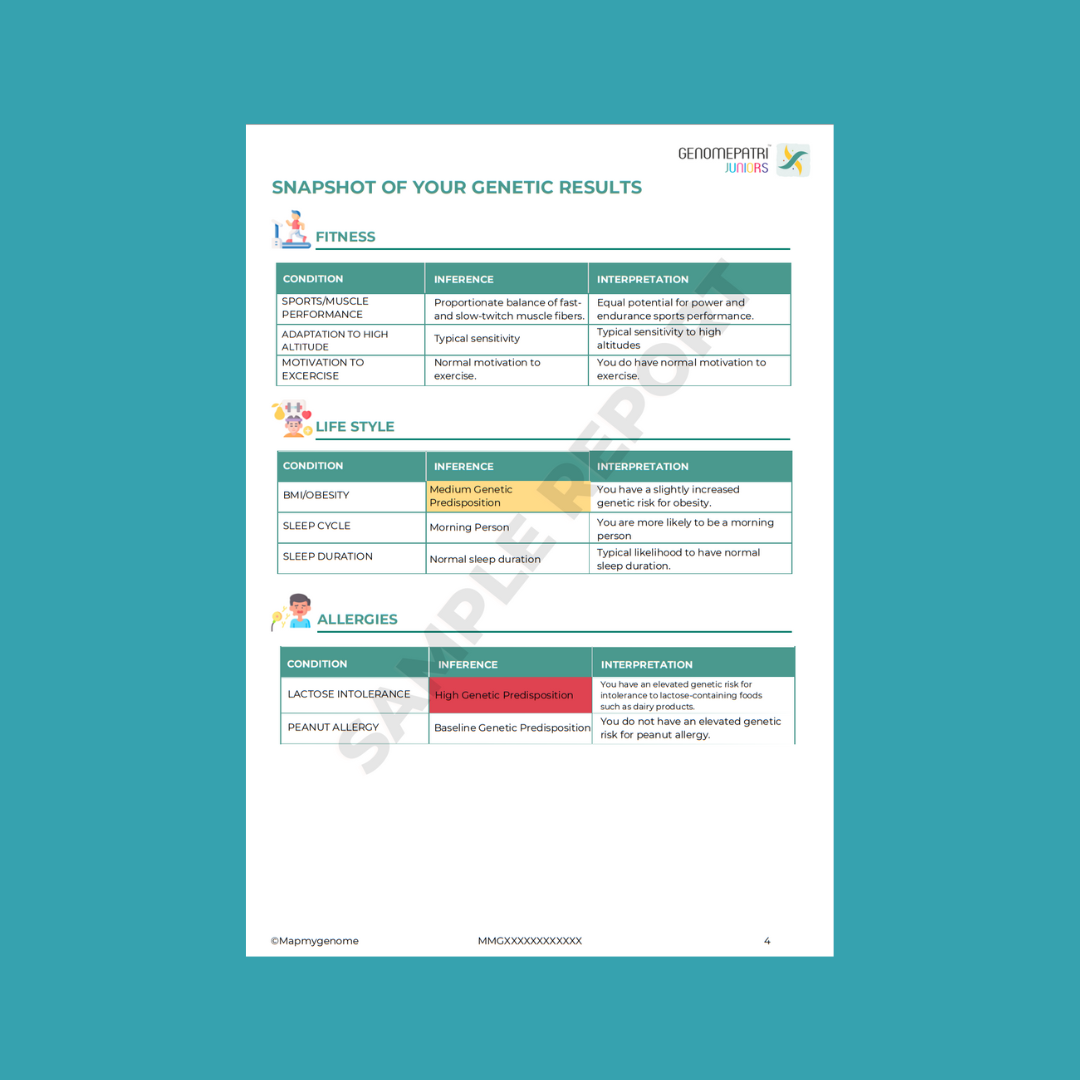
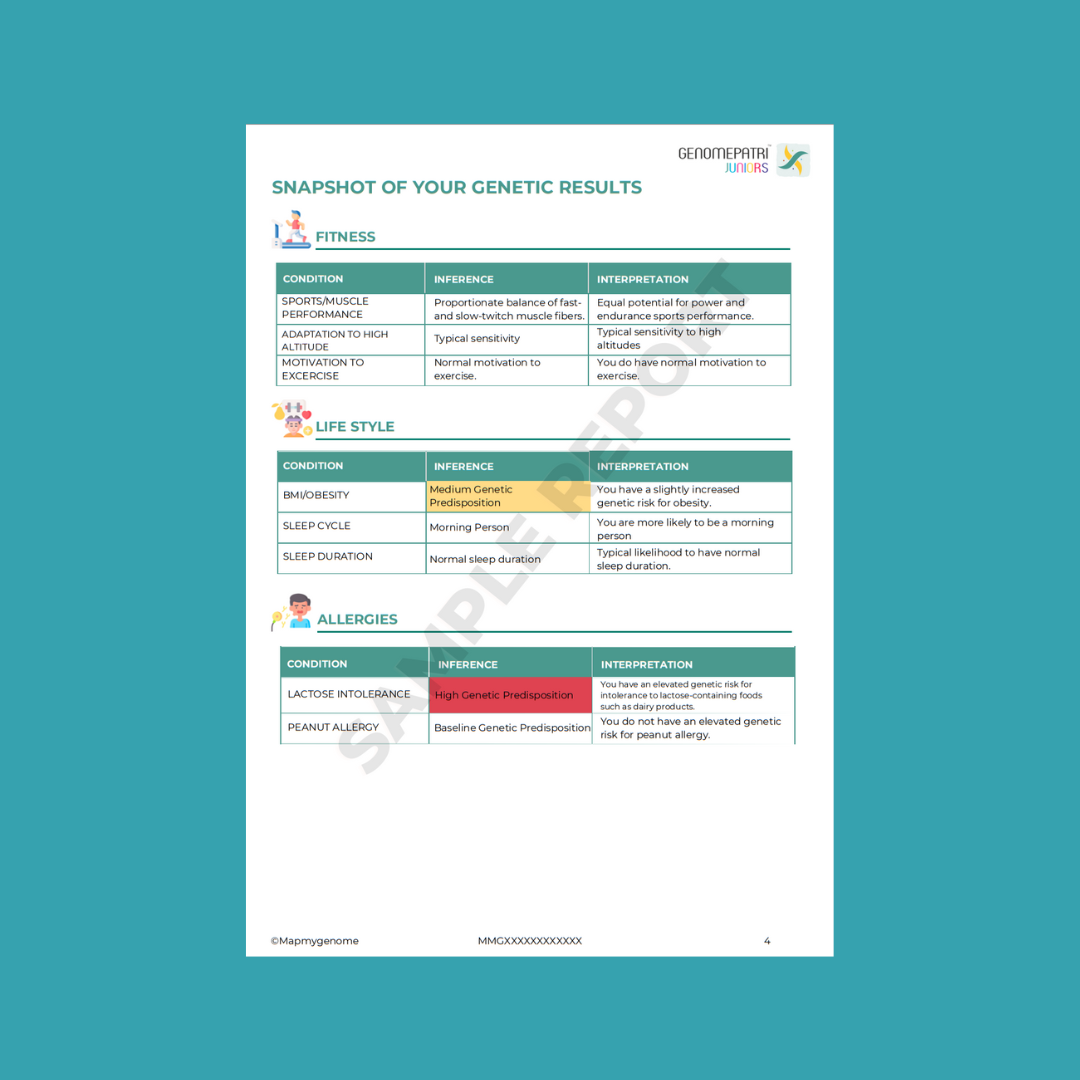
Genetic testing for children involves analyzing their DNA to detect genetic variants or mutations that could lead to health issues later in life. By understanding a child’s genetic makeup, parents and healthcare providers can identify potential health risks and take proactive measures to manage or prevent diseases.
This testing can focus on several areas, including:
- Hereditary diseases: Identifying genetic markers linked to inherited conditions.
- Metabolic disorders: Testing for abnormalities in the body's metabolic processes.
- Developmental delays: Understanding genetic factors contributing to developmental issues.
- Drug sensitivity: Assessing how a child's body may react to specific medications.
Benefits of Genetic Testing for Children
1. Early Detection of Health Risks
One of the primary benefits of pediatric genetic screening is the early detection of potential health risks. Genetic testing can reveal predispositions to conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and even some types of cancer. Detecting these risks early gives parents and healthcare providers the chance to implement lifestyle changes or monitoring protocols that could reduce the risk of these conditions developing or worsening.
2. Personalized Healthcare Plans
Genetic testing for children allows for the creation of personalized healthcare plans. Knowing a child's genetic predispositions can help doctors provide targeted recommendations for nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle. For example, if a child has a higher risk for obesity or cardiovascular disease, doctors can suggest a tailored diet and physical activity plan to mitigate these risks from an early age.
3. Targeted Monitoring and Screening
With insights from genetic testing, healthcare providers can implement targeted screening and monitoring for specific conditions. For instance, if a child is found to be at higher risk for developing a particular type of cancer, doctors may suggest regular screenings or advanced diagnostic tools to catch any signs early. Early intervention can drastically improve the chances of successful treatment.
4. Identification of Rare Genetic Disorders
Many rare genetic disorders can be identified through pediatric genetic testing, some of which may not show symptoms until much later in life. Early identification of these disorders allows parents to be prepared and take necessary actions, whether that involves treatments, lifestyle modifications, or seeking expert guidance for managing the condition.
5. Improved Drug Sensitivity and Dosing
Pharmacogenomics, a field of genetic testing focused on how individuals respond to medications, can be incredibly beneficial for children. By understanding how a child's body metabolizes certain drugs, doctors can tailor medication dosages more accurately and avoid adverse reactions. This is particularly valuable for children who may need regular medication or are dealing with chronic conditions.
Types of Genetic Testing for Children
There are various types of genetic tests available for children, each providing different kinds of insights into their health.
1. Newborn Screening
Newborn screening is a form of genetic testing that most babies undergo shortly after birth. This screening can detect genetic, metabolic, and developmental disorders that may not be immediately apparent. Conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and phenylketonuria (PKU) can be identified through newborn screening.
2. Carrier Testing
Carrier testing is another form of pediatric genetic screening that helps determine whether a child carries genes for certain inherited conditions, such as cystic fibrosis or Tay-Sachs disease. While being a carrier doesn’t necessarily mean the child will develop the disease, it’s valuable information for future family planning.
3. Diagnostic Testing
If a child exhibits symptoms of a genetic disorder, diagnostic genetic testing can help confirm the presence of a genetic mutation associated with that condition. This can be especially helpful for children who show developmental delays or have physical symptoms that suggest a genetic cause.
4. Predictive and Presymptomatic Testing
For children who have a family history of certain hereditary diseases, predictive testing can assess their risk of developing these conditions later in life. Presymptomatic testing is also available for conditions that may not manifest until adulthood, such as Huntington’s disease or certain types of cancer.
When to Consider Genetic Testing for Your Child
1. Family History of Genetic Conditions
If you or your partner have a family history of genetic disorders, it’s advisable to consider genetic testing for your child. Understanding their genetic risks can provide valuable information for managing and preventing potential health issues.
2. Unexplained Symptoms
If your child is experiencing unexplained symptoms, such as developmental delays, recurrent infections, or unusual physical traits, genetic testing could help identify the underlying cause.
3. Adoption
For parents who have adopted a child, genetic testing can provide insights into the child’s medical history, especially if the biological parents’ health information is not available.
The Ethical Considerations of Genetic Testing for Children
While genetic testing offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consider the ethical implications. Some concerns include:
- Privacy: Genetic data is highly personal, and parents must ensure that their child’s information is protected.
- Psychological Impact: Knowing about genetic risks at a young age may have psychological effects on both the child and the parents.
- Future Implications: Genetic testing results may affect the child’s future ability to obtain insurance or may raise questions about their career and lifestyle choices.
It’s essential to work with a genetic counselor to understand the potential implications of testing and to make informed decisions.
Conclusion: Investing in Your Child's Future Health
Genetic testing for children provides a proactive approach to managing health risks. From early detection of hereditary conditions to personalized healthcare strategies, the benefits are far-reaching. Parents can use this information to make informed decisions about their child's health and well-being, giving their children the best possible start in life.
If you're considering genetic testing for your child, consult with a healthcare professional or genetic counselor to discuss the best options based on your family's medical history and health concerns. Early knowledge is key to preventing and managing future health risks, ensuring a healthier, brighter future for your child.